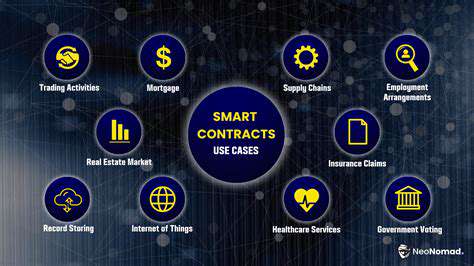
Smart Contracts for Automated Transactions
Smart Contracts: The Automation Revolution
Smart contracts are transforming transactional processes through code-based execution. These blockchain-stored agreements automate operations traditionally requiring intermediaries, creating streamlined workflows. This paradigm shift delivers substantial efficiency gains and cost reductions across multiple sectors. By removing human processing from transactional loops, smart contracts accelerate operations while minimizing security vulnerabilities.
The transparent nature of blockchain-hosted contracts ensures all participants can verify agreement terms. This visibility reduces disputes and builds trust, making smart contracts particularly valuable for supply chain coordination, identity management, and financial services applications.
Key Advantages of Smart Contract Implementation
Smart contracts excel at automating complex processes with precision. Their programmed execution eliminates human error while ensuring perfect adherence to predefined conditions. This reliability translates to significant time and resource savings across operational processes. The contracts' deterministic nature guarantees identical outcomes given the same inputs, creating predictable, audit-friendly transaction environments.
Blockchain's immutable ledger provides additional security benefits for smart contracts. Once deployed, contract terms become permanently recorded and unalterable, creating tamper-proof business logic. This characteristic, combined with complete transaction visibility, establishes unprecedented levels of accountability in automated systems.
Implementation Considerations and Obstacles
Despite their advantages, smart contract adoption faces technical hurdles. Security vulnerabilities in contract code can lead to catastrophic failures, necessitating rigorous auditing processes. The specialized nature of blockchain development often requires scarce expertise, creating implementation bottlenecks for many organizations.
Integration with legacy systems presents another significant challenge. Retrofitting existing infrastructure to accommodate smart contracts frequently demands extensive modifications. These technical transitions require careful planning to ensure compatibility while maintaining operational continuity during migration periods.
Emerging Applications and Transformative Potential
Smart contract applications continue expanding beyond financial technology. In logistics networks, these automated agreements can verify shipments, trigger payments, and maintain real-time inventory records without human oversight. Healthcare systems leverage them for secure medical data exchange while maintaining strict access controls.
The widespread adoption of smart contracts promises to redefine business operations. By combining process automation with cryptographic security, these tools enable new organizational models and create opportunities for unprecedented operational efficiency. As the technology matures, its impact across industries will likely accelerate dramatically.
Challenges and Future of Blockchain-Based Digital Asset Management
Scaling Digital Asset Networks
Blockchain networks face fundamental scaling limitations as adoption grows. Increased transaction volumes strain network capacity, causing processing delays and inflated fees. While solutions like layer-2 protocols and alternative consensus mechanisms show promise, they often involve compromises between decentralization, security, and performance that require careful evaluation.
Balancing Decentralization and Security
The decentralized ideal of blockchain presents unique security management challenges. Distributed control complicates coordinated responses to threats, while the pseudonymous nature of many networks creates accountability gaps. Emerging governance models attempt to reconcile these competing priorities through innovative voting mechanisms and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
The Interoperability Imperative
The proliferation of isolated blockchain networks creates digital asset silos that limit ecosystem potential. Developing cross-chain communication standards remains critical for enabling seamless asset transfers between different platforms. Standardized tokenization frameworks and universal wallet solutions are emerging to address these fragmentation issues.
Navigating Regulatory Landscapes
Digital asset regulations remain in flux across global jurisdictions. This uncertainty creates compliance challenges for businesses operating across borders. Regulatory clarity continues to emerge gradually, with frameworks evolving to address anti-money laundering (AML) requirements, investor protections, and taxation policies specific to blockchain assets.
Implementation Costs and Barriers
Enterprise blockchain adoption requires substantial infrastructure investments. Beyond initial development costs, organizations must account for ongoing maintenance, security audits, and personnel training. The specialized nature of distributed ledger technology creates steep learning curves that can slow organizational adoption timelines.
User Experience and Adoption Hurdles
Complex key management and technical jargon create significant barriers for mainstream users. Simplifying interfaces, improving educational materials, and developing intuitive wallet solutions are critical for broadening blockchain adoption beyond technical enthusiasts. Successful platforms will prioritize accessibility without compromising security fundamentals.
Evolving Security Threats
Despite blockchain's cryptographic foundations, digital asset platforms remain vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. Phishing schemes, smart contract exploits, and exchange hacks require continuous security innovation. Advanced monitoring systems, decentralized identity solutions, and formal verification methods are becoming essential components of comprehensive security strategies.