Immutability's Core Principles
Immutable records, at their heart, are data structures that cannot be modified after their creation. This fundamental characteristic is crucial for maintaining data integrity and preventing unintended side effects within applications. By ensuring data remains constant, developers can significantly reduce the risk of bugs stemming from unexpected modifications. This immutability is achieved through techniques like deep copying and avoiding direct manipulation of existing values.
The core principle behind immutability is to create a new record whenever a change is needed. This approach allows for complete control over data flow and facilitates the tracking and debugging of changes. This contrasts sharply with mutable records, which allow for direct alteration of existing data, potentially leading to subtle and hard-to-find errors.
Benefits of Using Immutable Records
The benefits of using immutable records extend beyond simply preventing accidental modifications. They enable easier reasoning about data transformations, making code more understandable and maintainable. This is because the state of a system can be precisely tracked without worrying about unexpected changes. Immutable records also promote concurrency, as multiple threads can safely access and modify the data without conflicting updates.
Furthermore, immutability often leads to more robust and reliable applications. By preventing unintended changes, the likelihood of bugs caused by data inconsistencies is reduced. This improved reliability directly translates to a more stable and predictable software system.
Data Integrity and Consistency
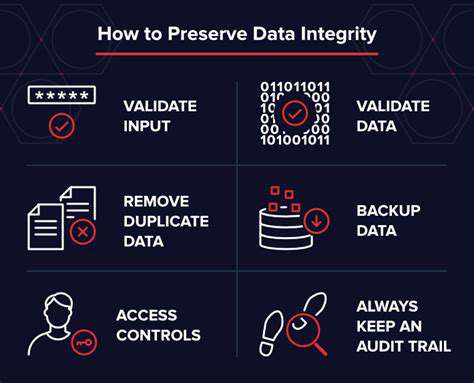
Immutable records are inherently tied to data integrity and consistency. Since the data cannot be altered after creation, any changes must be explicitly defined and managed, ensuring that the data always reflects the intended state. This meticulous approach to data management is particularly valuable in applications handling sensitive information or critical operations.
Maintaining consistent data across a system is simplified by immutability. This means that the data always remains accurate and reliable, eliminating the risk of errors stemming from conflicting or outdated data values.
Concurrency and Thread Safety
Immutable records are particularly well-suited for concurrent programming environments. Because data cannot be modified after creation, multiple threads can safely access and use the record without fear of data corruption. This inherent thread safety simplifies the development of concurrent applications, allowing developers to focus on the logic of their programs rather than managing complex synchronization mechanisms.
This inherent thread safety is a significant advantage, as it eliminates the need for complex locking mechanisms and reduces the chance of race conditions, a frequent source of errors in concurrent programs.
Versioning and History Tracking
Immutable records naturally lend themselves to versioning and history tracking. Each modification results in a new record, preserving the previous state. This historical record of changes allows for easier debugging, rollback capabilities, and a comprehensive understanding of the evolution of the data.
The ability to track changes is essential in many applications, especially in systems where data integrity and traceability are paramount. The immutability of records makes it straightforward to review the history of data modifications, enabling developers to pinpoint errors and understand the evolution of the system’s state.
Practical Applications and Implementations
Immutable records have a wide range of practical applications, from managing financial transactions to handling scientific data. In financial systems, immutability is crucial for ensuring the integrity of transactions and preventing fraud. Furthermore, in scientific research, immutable records can be used to manage experimental data, preventing inadvertent alterations and maintaining the accuracy of analysis.
Implementing immutable records can be achieved through various techniques, including functional programming paradigms and specialized libraries in many programming languages. These tools and methodologies provide developers with the necessary tools to harness the power of immutability in their applications.
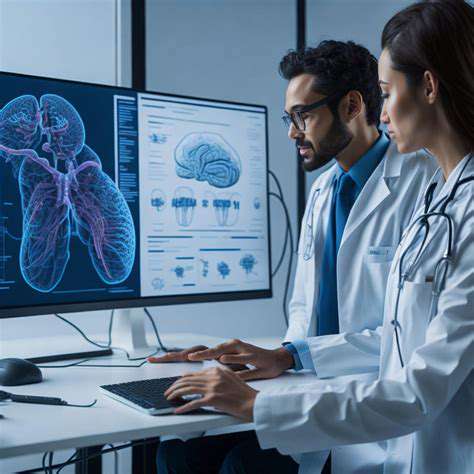
Autonomous systems, encompassing everything from self-driving cars to sophisticated robotic surgery tools, are rapidly proliferating across various sectors. This expansion presents both extraordinary opportunities and profound ethical challenges. The increasing complexity and autonomy of these systems demand careful consideration of the potential impacts on society, particularly concerning safety, accountability, and the very definition of human control in increasingly automated environments.