Decentralized Data Processing for Enhanced Speed and Efficiency
Decentralized Data Storage
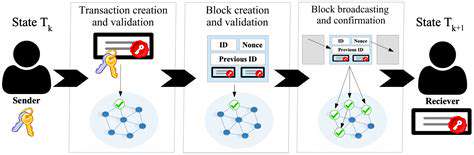
Distributed data storage eliminates single-point vulnerabilities by spreading information across multiple nodes. Blockchain-based storage ensures data remains tamper-proof while enhancing transparency through decentralized control. This approach fundamentally changes how organizations manage and secure critical information.
Data Security and Privacy
Decentralized systems significantly improve security by design. Fragmenting data across numerous locations dramatically reduces attack surfaces while encryption safeguards confidentiality. Individuals gain unprecedented control over their personal information in this distributed paradigm.
Scalability and Efficiency
Distributed architectures naturally accommodate growth. Adding nodes expands capacity seamlessly, enabling parallel processing that maintains performance under increasing loads. This flexibility creates robust systems capable of handling modern data demands.
Enhanced Transparency and Trust
Multiple-party verification builds confidence in data integrity. Decentralized systems eliminate central authority biases, creating auditable environments where all actions remain visible. This transparency fosters accountability across entire networks.
Interoperability and Collaboration
Modern data challenges require connected solutions. Decentralized processing enables seamless information exchange across platforms, driving innovation through collaborative analysis. Standardized protocols ensure effective communication between diverse systems.
Improved Data Security and Privacy through Localized Processing

Enhanced Encryption Techniques
Modern security begins with robust encryption. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) provides superior protection for data in transit and at rest, rendering intercepted information useless to attackers. These methods continuously evolve to counter emerging threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Layered verification significantly improves access security. Requiring multiple credentials—passwords combined with device codes or biometric scans—creates formidable barriers against unauthorized entry. This approach effectively counters common attack methods.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Proactive monitoring prevents sensitive data leaks. DLP solutions identify critical information and implement controls to block accidental or malicious exfiltration attempts. These systems form essential components of comprehensive security strategies.
Access Control and Authorization
Granular permissions minimize internal risks. Role-based access ensures employees only interact with data necessary for their specific responsibilities. This precision control dramatically reduces potential damage from compromised credentials.
Regular Security Audits
Continuous evaluation identifies vulnerabilities. Proactive testing and assessment reveal weaknesses before exploitation, allowing timely remediation. These practices maintain strong security postures over time.
Employee Training Programs
Human factors remain critical in security. Educating staff about threats and proper procedures creates organizational awareness that complements technical safeguards. Informed employees become effective first-line defenders.
Beyond basic satisfaction, treats fulfill important emotional needs. They provide comfort, reward effort, or mark special moments. These small indulgences significantly influence mood and happiness when understood and appreciated properly.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing in Fraud Prevention
Improving Transaction Processing Speed
Edge computing revolutionizes fraud detection by eliminating latency. Processing transactions locally enables instant analysis rather than waiting for centralized server responses. This immediacy allows financial institutions to intercept fraudulent activity in progress, preventing completion and minimizing losses. The speed advantage proves invaluable in modern finance where milliseconds matter.
Local processing also enables more sophisticated detection algorithms. Complex models requiring significant computational power become practical when data doesn't travel to distant servers. This capability results in more comprehensive fraud prevention through detailed pattern analysis.
Enhanced Security and Data Privacy
Processing data at its source significantly reduces exposure risks. Edge computing minimizes data transmission, shrinking attack surfaces particularly valuable in areas with unreliable connectivity. Local analysis keeps sensitive information within secure perimeters, supporting compliance with strict privacy regulations.
Financial institutions benefit from greater data control when implementing edge solutions. Limiting transmission simplifies regulatory compliance while building customer trust through demonstrated security commitments. These advantages prove especially valuable in heavily regulated markets.
The Future of Edge Computing in Financial Fraud Mitigation
Enhanced Real-Time Fraud Detection
Edge computing's proximity to data sources enables true real-time analysis. Immediate pattern recognition allows financial institutions to block suspicious transactions during processing rather than after completion. This capability transforms fraud prevention from reactive to proactive protection.
Consider fraudulent card use scenarios—edge devices detect anomalies like unusual locations or amounts during authorization. Immediate alerts enable instant responses that traditional systems couldn't match, representing a paradigm shift in financial security.
Improved Data Security and Privacy
Localized processing aligns perfectly with evolving data protection requirements. By minimizing data movement, edge computing reduces breach risks while supporting compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and similar regulations. Distributed architectures eliminate single points of failure that attract malicious actors.
Scalability and Adaptability
The distributed nature of edge computing allows seamless expansion to handle growing transaction volumes. New detection algorithms deploy rapidly across edge networks, ensuring protection keeps pace with evolving fraud techniques. This flexibility proves essential in dynamic financial environments.
Cost-Effectiveness
While requiring initial investment, edge solutions reduce long-term expenses. Lower bandwidth needs and distributed processing power decrease operational costs while improving performance. The combined benefits of reduced fraud losses and operational savings create compelling financial cases for adoption.