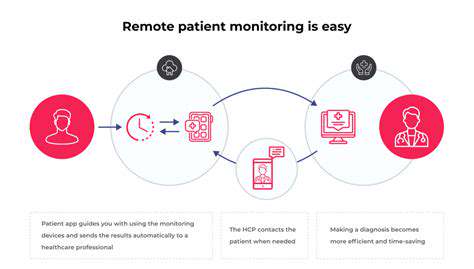
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling continuous health data collection and analysis, leading to earlier detection of potential health issues and improved preventative care. This proactive approach, enabled by technology, allows healthcare providers to intervene earlier and more effectively, significantly reducing the risk of complications and hospitalizations. Furthermore, the ability to monitor patients remotely facilitates better management of chronic conditions, empowering patients to actively participate in their care and improving adherence to treatment plans.
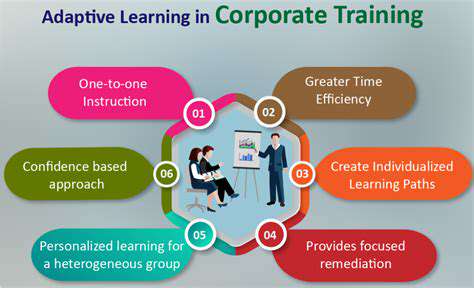
Tailoring VR Experiences to Individual Needs
Understanding User Needs
A crucial aspect of successful VR experience design is a deep understanding of the diverse needs and preferences of individual users. This includes considering factors like age, physical abilities, prior experience with VR technology, and even psychological predispositions. Developing a user persona is essential for this, allowing developers to create experiences tailored to specific demographics and use cases. Identifying common pain points and positive interactions within a user group is vital to creating a truly immersive and engaging experience.
Personalized Content Delivery
Personalization goes beyond simply adjusting difficulty levels. It should encompass dynamic content selection, tailored narratives, and interactive elements that adapt to the user's real-time actions and reactions. For example, a virtual museum experience could dynamically adjust the exhibit selection based on the user's prior interests or the pace at which they are exploring the environment. This level of adaptability enhances user engagement and provides a more enriching experience overall.
Adaptive Difficulty and Pace
Tailoring the difficulty and pace of VR experiences is crucial for inclusivity and engagement. A complex simulation should offer adjustable difficulty settings, allowing users to modify the challenge based on their skill level and experience. Similarly, the pace of the experience should be flexible, allowing users to control the speed of their interaction and exploration. This accommodates individuals with varying levels of comfort and confidence with technology.
Accessibility Considerations
VR experiences should be designed with accessibility in mind, considering the needs of users with disabilities. This encompasses features like alternative input methods (e.g., voice commands, eye tracking), adjustable visual and auditory settings, and clear and concise on-screen text. Prioritizing accessibility ensures that a wider range of users can fully participate in and benefit from the experience. It also demonstrates a commitment to inclusive design principles.
Emotional Responses and Feedback
VR experiences have the potential to evoke a wide range of emotional responses. Therefore, developers should design mechanisms to gauge user reactions and provide appropriate feedback. This might involve detecting signs of discomfort or disorientation and offering support or alternative approaches. A thoughtful approach to emotional responses can improve the overall user experience and promote a more positive and safe environment within the virtual world.
Tracking User Progress and Preferences
Effective VR experiences often require a certain level of user engagement and progression. Robust tracking mechanisms can monitor user interactions, identify patterns of behavior, and gather feedback. This data can then be used to refine the experience over time, offering personalized recommendations and adjusting content based on individual preferences. By continuously monitoring user engagement, developers can create experiences that are genuinely responsive and adaptive to individual needs.
Iterative Design and Feedback Loops
Developing effective VR experiences is an iterative process. Regular feedback from users is essential to identify areas for improvement and refine the design. This feedback can come from various sources, including user surveys, focus groups, and direct interaction with the VR environment. Gathering and analyzing this feedback within a well-defined process can significantly enhance the VR experience over multiple iterations. This iterative approach is crucial for optimizing the user experience and creating a truly engaging and personalized virtual world.