Introduction to Patient Flow and the Role of AI
Understanding Patient Flow
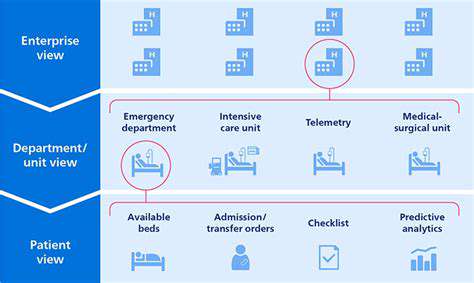
Patient flow, in healthcare settings, describes how patients move through different care stages, starting from their first contact until discharge. This process involves multiple steps like appointment scheduling, paperwork completion, diagnostic tests, treatment administration, and final discharge. A well-managed patient flow system is fundamental for delivering high-quality care and ensuring patients leave satisfied. When patient flow improves, healthcare facilities operate more efficiently and effectively.
Grasping the complexities of patient flow helps optimize resource use, simplify processes, and cut down wait times. Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare environments each have distinct patient flow patterns. Examining these patterns reveals bottlenecks and allows for targeted improvements to enhance the patient experience.
Key Elements of Patient Flow
Several components are essential for an efficient patient flow system. These include reliable scheduling methods, streamlined administrative tasks, clear pathways tailored to different patient types, and appropriate staffing levels. Mastering these elements ensures patients receive timely and suitable care.
Simplifying these components reduces patient wait times and boosts satisfaction. Effective communication between departments and providers is vital for smooth transitions between care stages. Technology also plays a crucial role by managing records and appointments, increasing overall efficiency.
Impact on Patient Experience
An organized patient flow system directly affects how patients perceive their care. Patients who encounter minimal delays and clear communication feel more comfortable, informed, and valued. This positive experience fosters higher satisfaction and loyalty toward the healthcare provider.
On the other hand, poor patient flow leads to frustration, anxiety, and dissatisfaction. Long wait times, confusing instructions, and inadequate communication can damage trust in the facility. Addressing these issues is key to maintaining a strong reputation.
Challenges in Optimizing Patient Flow
Optimizing patient flow comes with obstacles, such as unpredictable patient volumes, varying patient needs, and strict regulatory requirements. Introducing new technologies and processes while maintaining care quality adds complexity.
Staff shortages, especially in administrative roles, can disrupt patient flow. Developing solutions for these challenges ensures a seamless patient journey. Adapting to evolving healthcare demands and ensuring smooth transitions between care settings are equally important.
Technology and Patient Flow Management
Technology significantly enhances patient flow management. Electronic health records (EHRs), scheduling software, and patient portals simplify administrative tasks, reduce paperwork, and improve communication. These tools help healthcare providers allocate resources more efficiently and refine patient care pathways.
Data analytics can monitor patient flow patterns to identify and resolve bottlenecks. Recognizing trends allows facilities to proactively adjust processes for better efficiency. This proactive strategy ensures a smoother, more effective patient experience.
Data Sources and Integration for AI-driven Insights
Data Sources for Patient Flow Analytics
AI-driven patient flow insights depend on diverse data sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), administrative systems, patient portals, and real-time sensor data from hospital equipment. Combining these sources provides a complete view of patient journeys. Structured data, like demographics and diagnoses, alongside unstructured data, such as physician notes and patient feedback, offers a thorough understanding of patient needs and experiences.
Extracting relevant information requires careful data cleaning and transformation. Standardizing formats and addressing missing data ensures AI algorithms can process the information accurately, yielding reliable insights.
EHR Integration and Data Extraction
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are a primary data source for patient flow analysis. Extracting details like admission and discharge dates, procedures, and diagnoses is essential. This process must comply with HIPAA regulations to protect patient privacy. Proper data extraction helps visualize patient journeys and identify bottlenecks.
Integration of Administrative Data
Administrative data, such as billing and insurance records, adds context to patient flow. Merging this with EHR data reveals trends in care access and financial impacts. This integration provides a broader view of the patient journey, covering clinical, financial, and administrative aspects.
Real-Time Sensor Data Integration
Real-time sensor data from hospital equipment, like bed occupancy and waiting room monitors, offers insights into current patient flow dynamics. This data enables proactive management of queues and resource allocation, creating a more responsive system.
Patient Portal and Feedback Data
Patient portals and feedback tools capture patient perspectives on their experiences. Analyzing this data highlights satisfaction levels, perceived wait times, and system pain points. Integrating this feedback with clinical and administrative data creates a more complete picture of the patient journey and identifies improvement areas.
Data Standardization and Transformation
Data consistency and accuracy are vital for AI analysis. Standardization converts data from various sources into a uniform format. Transformation involves handling missing values, fixing inconsistencies, and normalizing data. These steps ensure reliable datasets for AI models, leading to meaningful results.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations
Protecting patient data is critical. Compliance with HIPAA and other privacy regulations is mandatory during data collection, integration, and analysis. Strong security measures, such as encryption and access controls, prevent unauthorized access. Data anonymization safeguards patient privacy while enabling analysis. These steps maintain trust and legal compliance.
Improving Patient Experience and Reducing Costs with AI
Optimizing Patient Check-in and Scheduling
AI-powered check-in and scheduling systems enhance patient experience by reducing wait times. These systems analyze historical data to predict busy periods, adjust appointment availability, and notify patients of delays. This proactive approach minimizes frustration and maximizes efficiency.
AI can also personalize scheduling based on patient needs, such as prioritizing those with mobility challenges. This customization creates a more welcoming environment.
Predictive Modeling for Patient Flow
AI algorithms analyze patient data to predict flow patterns. Identifying bottlenecks and volume surges allows providers to adjust staffing and resources, preventing unnecessary delays.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy and Speed
AI aids in diagnostics by analyzing medical images, lab results, and records to detect anomalies. This leads to faster, more accurate diagnoses, earlier interventions, and better outcomes. Quick diagnostics are especially crucial in emergencies, saving lives and reducing hospital stays.
Personalized Treatment Plans and Recommendations
AI generates tailored treatment plans by considering patient history and preferences. This personalization improves adherence and outcomes.
Enhanced Resource Allocation and Staff Optimization
AI analytics optimize resource use across departments. Monitoring patient flow and predicting needs helps administrators make data-driven decisions on staffing and equipment. This efficiency reduces waste and maximizes funds.
Reducing Administrative Burden and Costs
AI automates tasks like scheduling, claims processing, and record management, freeing staff for patient care. This automation cuts costs and improves efficiency, allowing reinvestment in patient care.