The Rise of AI-Powered Fashion Design Tools
The Algorithmic Muse
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the fashion industry, moving beyond simple trend forecasting to encompass the entire design and production process. AI-powered tools now analyze vast datasets of consumer preferences, historical trends, and social media buzz to predict styles that will resonate with audiences. This enables designers to create collections that are both aesthetically compelling and commercially successful, reducing risk while boosting profitability.
This data-driven approach to fashion design marks the beginning of a new era in personalization. AI can customize garments to individual body types and style preferences, offering a genuinely bespoke experience. This shift moves the industry away from mass production toward a more refined and individualized approach.
Personalized Experiences
One of AI's most notable contributions to fashion is its ability to tailor the shopping journey. AI-driven chatbots provide instant assistance, answering queries about sizing, fabric choices, and care instructions in real time. This level of personalized service enhances customer satisfaction while fostering stronger brand loyalty.
Sustainable Innovation
AI is also instrumental in advancing sustainability within fashion. By optimizing material usage and predicting waste, AI helps minimize the environmental footprint of garment production. This represents a critical step toward a more eco-conscious industry that prioritizes sustainable practices.
Additionally, AI facilitates the discovery of innovative, sustainable materials. By evaluating fabric properties and identifying alternatives to harmful substances, AI accelerates the development of greener textile solutions.
Streamlined Production
AI is revolutionizing manufacturing processes. From optimizing workflows to anticipating production bottlenecks, AI enhances efficiency across the board. These improvements lead to reduced costs, making fashion more accessible to broader audiences.
AI systems can also monitor production lines in real time, identifying and correcting errors immediately. This proactive quality control approach decreases defects and waste, contributing to a more efficient supply chain.
Enhanced Design Tools
AI is redefining how designers work by providing advanced tools for concept development. These systems can generate design variations, suggest color schemes, and even create complete collections based on specified parameters. Such capabilities empower designers to explore creative possibilities and push the boundaries of fashion.
The Future of Fashion
While AI's integration into fashion is still evolving, its potential impact is unmistakable. As AI technology progresses, we can anticipate even more innovative applications that will reshape how fashion is designed, produced, and consumed. The result will be a more sustainable, personalized, and inclusive fashion landscape.
The future of fashion is inextricably linked to AI's advancement, promising a more dynamic, efficient, and responsible industry in the years ahead.
Ethical Considerations
The rise of AI in fashion brings exciting opportunities but also necessitates careful ethical examination. Issues like job displacement and algorithmic bias require thoughtful consideration. Maintaining ethical standards and ensuring fair distribution of benefits is crucial as the industry navigates this technological transformation. Transparency and accountability in AI applications will be vital.
Furthermore, developing ethical guidelines and regulations is essential to ensure AI is used responsibly and doesn't reinforce existing industry inequities.

Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Bias and Representation in AI-Generated Designs
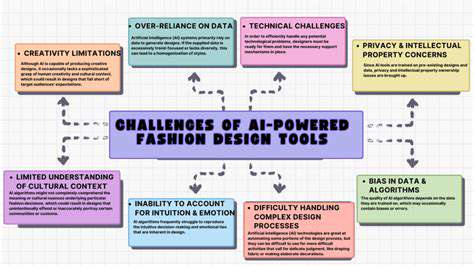
A significant concern with generative AI in fashion is its potential to perpetuate societal biases. Since AI models learn from existing datasets, any historical inequalities or stereotypes in the data may be reflected in the designs. For instance, if training data primarily features Western aesthetics and body types, the AI might produce designs that exclude diverse cultures and shapes. This could marginalize certain communities and limit creative innovation.
To counter this, developers must prioritize diverse representation in training data and actively challenge stereotypes. Ongoing monitoring of AI outputs is also necessary to identify and address emerging biases.
Intellectual Property Rights and Ownership
Generative AI raises complex questions about intellectual property. When an AI creates a design, ownership becomes ambiguous—does it belong to the designer who prompted the AI, the company that developed the model, or the AI itself? Clear legal frameworks are needed to resolve these issues and ensure transparency.
Without established guidelines, disputes may arise, potentially hindering broader adoption of generative AI. Robust intellectual property policies are essential to encourage innovation and collaboration between designers and AI tools.
The Impact on Human Designers
The integration of generative AI poses challenges for human designers, particularly regarding job displacement as automation handles repetitive tasks. However, this shift also presents opportunities. Designers can focus on higher-level creative work, such as conceptualizing new ideas, refining brand identities, and tailoring AI-generated designs to specific needs.
The role of human designers in this evolving landscape is still taking shape. Success will require a shift toward strategic and conceptual thinking, with continuous learning and adaptation becoming key to thriving alongside AI.
Accessibility and Cost
Advanced generative AI tools may not be equally accessible to all designers. High computational costs and technical expertise requirements could disadvantage smaller studios or independent creators. Ensuring equitable access to these technologies is vital to foster innovation and prevent further marginalization within the industry.
Data Privacy and Security
Generative AI relies on extensive datasets of fashion designs and customer information. Protecting this data from unauthorized access and misuse is critical. Strong security measures must be implemented to safeguard intellectual property and personal data.
The Environmental Impact
The energy demands of training and running AI models raise environmental concerns. The fashion industry must address this by optimizing algorithms, using sustainable energy sources, and adopting energy-efficient infrastructure.
Designers and companies have a responsibility to minimize the environmental impact of AI integration. Embracing sustainable practices will be essential to mitigate the technology's ecological footprint.
Creativity and Originality
A key question is whether AI-generated designs can truly be original and creative. While AI excels at combining existing ideas, the essence of creativity often stems from human intuition and emotional depth. It's important to view AI as a tool that complements, rather than replaces, human creativity.
The ideal approach is to use AI for rapid prototyping and exploration, allowing designers to focus on the unique aspects of their vision. Combining human and artificial intelligence will be crucial for achieving groundbreaking fashion designs.