Engaging Learners Through Interactive Experiences
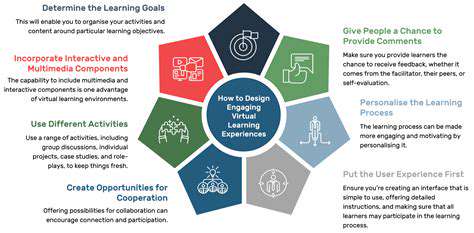
Interactive Learning Platforms
Today's education landscape is being transformed by interactive learning platforms that shift away from passive learning. These vibrant environments promote active engagement, empowering students to delve into concepts, tackle problems, and interact with materials more profoundly. Hands-on tools like simulations and virtual labs create tangible experiences, effectively connecting theoretical knowledge with practical application. This method proves especially beneficial for those who learn best through visual or physical engagement.
One standout advantage is the customization these platforms offer. Adaptive technologies pinpoint student challenges and deliver focused assistance, ensuring each learner progresses comfortably while building a thorough grasp of subjects. Such tailored approaches dramatically improve both engagement levels and knowledge retention.
Gamification Techniques
Introducing game elements into education can remarkably enhance student motivation. Reward systems like points, badges, and leaderboards foster healthy competition and achievement, turning learning into an enjoyable pursuit. This playful methodology inspires active participation and continuous self-improvement.
Game-inspired structures such as quests and level progression also cultivate analytical abilities. These features promote exploration, creative problem-solving, and strategic planning – skills that translate directly to real-world situations while deepening subject comprehension.
Collaborative Learning Environments
Student collaboration is fundamental for developing analytical and problem-solving capabilities. Modern platforms incorporate tools for group projects, discussion spaces, and peer learning opportunities. These cooperative settings allow for idea exchange, perspective challenges, and mutual learning, all of which enhance understanding while honing communication skills.
Through group assignments and digital discussions, students refine teamwork abilities and learn to collaborate across diverse groups. Explaining concepts to peers and defending viewpoints reinforces personal understanding while sharpening communicative competence.
Utilizing Multimedia Resources
Contemporary learning systems integrate varied media formats – videos, audio, animations, and imagery – to boost engagement and accessibility. Visually compelling content simplifies complex information, making it more digestible and memorable. By presenting material in multiple formats, these platforms effectively accommodate different learning preferences.
High-quality multimedia components create vibrant, immersive educational experiences. Captivating visuals and interactive features make learning more attractive and stimulating, maintaining student focus while promoting deeper subject mastery.
Real-World Applications and Simulations
Linking education to practical situations makes learning more relevant and impactful. Interactive simulations and virtual labs let students experiment with concepts in realistic settings, strengthening comprehension and analytical skills. These applications offer risk-free environments for experimentation and problem-solving, enabling students to bridge theory and practice.
Practical examples include medical procedure simulations, engineering prototypes, or historical recreations. Engaging with these scenarios allows students to learn through trial and error, building a robust foundation for future endeavors.
Measuring Impact and Providing Valuable Data
Measuring the Impact of Interventions
Accurately assessing intervention effectiveness demands a rigorous measurement approach. This begins with establishing clear, quantifiable goals and developing appropriate tracking metrics. The measurement framework must account for the intervention's specific context and target audience to ensure metric relevance. Properly designed evaluation systems enable comprehensive effectiveness assessments and highlight improvement areas.
Consistent monitoring is equally vital. Reliable data collection ensures accurate impact representation, while analysis reveals patterns, trends, and unexpected outcomes that may necessitate intervention adjustments.
Providing Value-Added Services
Supplementary services enhance core offerings by delivering additional support and resources that elevate user experience and results. These often include customized solutions and personalized assistance addressing specific requirements. Such enhancements can substantially increase perceived value and utility.
Effective implementation requires deep understanding of audience needs. Continuous feedback collection and evaluation ensure services remain relevant and adapt to evolving demands, facilitating ongoing refinement.
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing clear KPIs is foundational for meaningful impact measurement. These should follow SMART criteria – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Well-constructed KPIs provide concrete success benchmarks and enable progress tracking. Without them, accurately assessing initiative impact becomes challenging.
Selecting appropriate KPIs demands careful alignment with intervention objectives. Chosen metrics must directly reflect desired outcomes while offering practical progress measurement.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods
Method selection should align with intervention characteristics and information requirements. Options include surveys, interviews, focus groups, observational studies, or existing data analysis. Data quality assurance is paramount for reliable analysis and valid conclusions.
Comprehensive data examination is essential for drawing meaningful impact conclusions. Combining qualitative and quantitative analytical techniques reveals trends, patterns, and relationships, yielding deeper understanding of effectiveness.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Effective stakeholder involvement is critical for successful impact measurement and value delivery. Maintaining open communication channels builds trust and ensures goal alignment. Regular updates about progress, challenges, and findings promote transparency and accountability.
This approach secures broad support while allowing valuable stakeholder input that can significantly enhance interventions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Return on Investment
Financial evaluation through cost-benefit analysis assesses intervention viability by comparing expenditures to potential gains. Quantifying these elements enables informed resource allocation decisions and prioritization of high-return initiatives.
Thorough analysis justifies investments, demonstrates value, and ensures efficient resource use while identifying cost-reduction opportunities that maximize impact.
Reporting and Dissemination of Findings
Regular impact reporting maintains transparency and accountability. Clear, concise reports should communicate findings to stakeholders and broader audiences, facilitating knowledge sharing and learning from both successes and shortcomings. These insights can guide future interventions and policy development.
Effective dissemination through presentations, publications, or digital platforms ensures widespread access to valuable lessons that can inform and improve subsequent initiatives.