The Benefits of Edge Computing for AI
Decentralized Data Processing
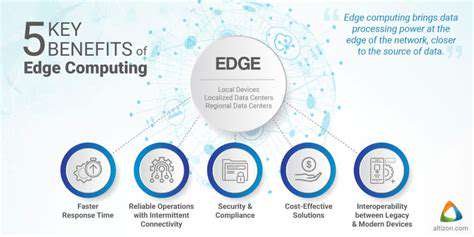
Edge computing fundamentally shifts data processing away from centralized servers, bringing it closer to the source of data generation. This decentralization offers significant advantages in terms of latency reduction, as data doesn't need to travel long distances to be processed. This proximity to the data source enables real-time responses and quicker decision-making, which is crucial for applications demanding immediate feedback.
Improved Responsiveness and Latency
One of the most compelling benefits of edge computing is its ability to drastically reduce latency. By processing data closer to the source, the time it takes for data to travel to a central server and back is minimized. This improvement is particularly vital for applications requiring rapid responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real-time video streaming. Reduced latency translates to smoother user experiences and more efficient operations.
Enhanced Security
By keeping data closer to its source, edge computing reduces the attack surface for potential cyber threats. Data is processed and stored locally, minimizing the risk associated with transmitting sensitive information across large networks. This localized processing enhances overall security posture, protecting sensitive information from breaches that could occur during transmission to remote servers. Data breaches can have significant consequences for individuals and organizations alike.
Increased Reliability and Resilience
Edge computing's decentralized nature enhances reliability and resilience in various scenarios. If a central server experiences an outage, edge devices can continue to operate independently. This distributed architecture ensures that critical services remain available even during network disruptions or other unforeseen events. This decentralized nature is a critical factor in ensuring continued operation during emergencies.
Cost Efficiency
While initial investment in edge infrastructure might seem higher compared to a centralized system, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. The reduced need for high-bandwidth communication links between edge devices and the cloud significantly lowers bandwidth costs. This cost-effectiveness is significant for organizations with large-scale deployments, and reduces the financial burden associated with data transmission. Lower bandwidth consumption also contributes to reduced energy costs.
Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Adding new edge devices and expanding data processing capabilities is relatively straightforward. This adaptability is particularly useful for rapidly evolving or growing organizations that need to adapt to changing demands and data volumes. Deployment of new applications and services is also easier and faster.
Optimized Data Management
Edge computing enables optimized data management by processing only the necessary data at the edge. This approach reduces the amount of data transmitted to the cloud and minimizes storage costs. Furthermore, this approach can reduce the need for extensive data backups and recovery procedures. This strategy is particularly effective for applications that generate massive volumes of data but only require a subset of it for analysis. This approach significantly streamlines data management.
Key Applications of Edge Intelligence
Real-time Data Processing
Edge intelligence excels at processing data in real-time, enabling immediate responses to events. This capability is crucial for applications requiring rapid reaction times, such as autonomous vehicles reacting to changing road conditions or industrial equipment monitoring for anomalies. Real-time Data Processing significantly reduces latency, enabling faster decision-making and improved efficiency. By processing information at the edge, valuable insights can be derived and acted upon almost instantaneously, avoiding delays caused by transmitting data to a central server.
Improved Security
Data privacy and security are paramount, and edge intelligence plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information. By processing data locally, edge devices can limit the transmission of sensitive data across networks, minimizing the risk of breaches or unauthorized access. This localized processing also strengthens security posture by reducing the attack surface for potential cyber threats. Data is less vulnerable to interception or manipulation as it doesn't need to travel far.
Edge devices can often employ more robust local security measures to protect data before it even leaves the device.
Enhanced Reliability
Edge computing minimizes reliance on centralized systems, bolstering the resilience and reliability of applications. This decentralized architecture is particularly valuable in situations where network connectivity is unreliable or intermittent, such as remote locations or emergency situations. Edge devices can function independently, even when the central network is unavailable. This ensures uninterrupted operation and critical services can continue.
Reduced Latency
A major advantage of edge intelligence is its ability to drastically reduce latency. By processing data closer to its source, edge devices minimize the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination. This is crucial for applications like video streaming, gaming, and industrial control systems, where even a slight delay can significantly impact the user experience or operational efficiency. Reduced latency also enhances responsiveness and improves overall performance.
Optimized Resource Utilization
Edge intelligence can significantly optimize resource utilization, particularly in scenarios with limited bandwidth or processing power. Instead of sending massive amounts of data to a central server, edge devices process only the necessary information, reducing the load on the network infrastructure. This efficient handling of data minimizes the need for high-capacity servers, which translates to lower costs and a smaller carbon footprint. By reducing the amount of data transmitted, edge computing helps conserve network resources and potentially reduce energy consumption.
The Technological Foundation of Edge Intelligence
The Rise of Decentralized Computing
Edge intelligence, at its core, represents a significant shift away from traditional centralized data processing architectures. Instead of relying on massive data centers located far from the source of the data, edge devices, such as smartphones, IoT sensors, and industrial machines, perform computations closer to the data's origin. This decentralized approach significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time responses and fostering a more dynamic and adaptive data-processing environment. This localized processing also enhances privacy and security by minimizing the transmission of sensitive information over potentially vulnerable networks.
Hardware Advancements: Powering Edge Capabilities
The advancements in microchip technology, particularly in areas like field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), are crucial to the success of edge intelligence. These specialized hardware components are designed to handle specific tasks efficiently and with low power consumption, making them ideal for deployment in resource-constrained environments. The miniaturization of these components allows for more widespread integration into various devices, further supporting the proliferation of edge intelligence applications.
Data Compression and Transmission Optimization
The volume of data generated by edge devices can be substantial. Efficient data compression techniques and optimized transmission protocols are essential to overcome bandwidth limitations and ensure seamless data transfer to central servers or other processing nodes. These techniques not only reduce data transfer times but also lower the cost of communication, making edge intelligence solutions more economically viable for a wider range of applications. This optimization is critical for maintaining responsiveness and scalability in edge computing environments.
AI Model Deployment and Optimization
Deploying and optimizing AI models on edge devices demands specialized techniques. The models need to be lightweight and adaptable to the computational constraints of various edge devices. Techniques like model quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation are employed to reduce model size and computational complexity, ensuring efficient execution on resource-limited hardware. This optimization process is critical for maintaining the accuracy and performance of AI capabilities while minimizing the strain on edge devices.
Security Considerations in Edge Computing
The distributed nature of edge intelligence introduces new security challenges. Protecting data at the edge requires robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. Ensuring the security of edge devices and the data they handle is paramount to prevent breaches and maintain the integrity of the system. These security considerations are especially critical in sensitive applications like healthcare and finance.
Software Frameworks and Development Tools
The development and deployment of edge intelligence solutions rely heavily on robust software frameworks and development tools. These tools provide developers with standardized interfaces, libraries, and APIs to simplify the process of building and deploying AI models and applications on edge devices. The availability of user-friendly tools will accelerate the innovation and adoption of edge intelligence solutions across various industries. This will facilitate a faster development cycle for edge-based applications.
Real-World Applications and Impact
Edge intelligence is already impacting a wide range of sectors. From autonomous vehicles that make real-time driving decisions based on sensor data to smart factories optimizing production processes, the applications are diverse and transformative. Edge intelligence enables real-time analysis and response, allowing for faster decision-making and improved efficiency in various industries. This technology is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the world around us, creating opportunities for innovation and productivity across numerous fields.