The Rise of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Core Components of IoMT
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) encompasses a vast network of interconnected medical devices, sensors, and applications. These devices collect, transmit, and analyze patient data, facilitating real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans. This interconnectivity is crucial for improving patient outcomes and streamlining healthcare operations. From wearable fitness trackers capable of monitoring vital signs to sophisticated implantable devices that deliver targeted drug therapies, IoMT devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated and versatile.
Central to the IoMT ecosystem are the various sensors and actuators that capture and respond to physiological data. These components range from simple temperature sensors to complex imaging devices, each playing a critical role in the overall functioning of the system. The integration of these diverse components allows for a comprehensive understanding of patient health, empowering healthcare professionals with valuable insights.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery
The integration of IoMT technology is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, enabling remote patient monitoring, facilitating faster diagnoses, and ultimately improving patient outcomes. The ability to monitor patients remotely is crucial for managing chronic conditions, enabling proactive interventions and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits. This approach not only saves time and resources but also enhances patient comfort and convenience.
Furthermore, IoMT fosters a more collaborative environment among healthcare providers. Data sharing and real-time communication between doctors, nurses, and specialists become significantly easier and more efficient. This enhanced communication streamlines care pathways, leading to faster interventions and better coordination of treatment plans. Ultimately, this results in more effective and personalized care for patients.
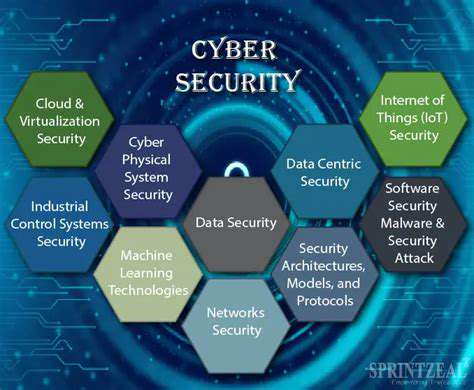
Security and Privacy Concerns
The increasing reliance on IoMT devices raises significant security and privacy concerns. The sensitive nature of the data collected by these devices necessitates robust security measures to protect patient information from unauthorized access or breaches. Data encryption, secure communication protocols, and access controls are crucial for safeguarding patient confidentiality and ensuring the integrity of the data.
Addressing these concerns requires a multi-faceted approach that involves not only technological advancements but also stringent regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Healthcare providers and device manufacturers must work collaboratively to establish and implement comprehensive security protocols that effectively mitigate risks and protect patient data from potential threats.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of IoMT holds immense potential for innovation and advancement in healthcare delivery. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms with IoMT devices promises to enhance diagnostic capabilities, personalize treatment plans, and predict potential health risks. AI-powered analysis of patient data can provide valuable insights, enabling earlier interventions and potentially preventing serious health complications.
Furthermore, the development of more sophisticated and user-friendly IoMT devices will lead to wider adoption and increased accessibility. This will enable more patients to benefit from remote monitoring and personalized care, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Continued advancements in wireless communication technologies will also play a crucial role in facilitating seamless data transmission and reducing latency, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Data-Driven Insights for Personalized Care
Leveraging IoT for Tailored Treatment Plans
Data-driven insights gleaned from IoT devices in healthcare, particularly in the realm of IoMT (Internet of Medical Things), empower healthcare providers to craft highly personalized treatment plans. By monitoring patients' vital signs, activity levels, and other relevant data in real-time, doctors can gain a comprehensive understanding of individual patient needs and tailor interventions accordingly. This personalized approach fosters better patient outcomes and enhances the overall quality of care.
This goes beyond simply reacting to a symptom; it allows proactive intervention. For instance, if a patient with a history of heart conditions exhibits subtle changes in their heart rate or blood pressure patterns, the IoMT device can alert the medical team, potentially preventing a serious incident before it occurs. This predictive capability is a significant advantage of incorporating IoT into healthcare.
Improving Patient Engagement and Adherence
Personalized insights not only benefit healthcare professionals but also empower patients. By providing patients with access to their own health data and interactive tools, IoMT devices foster a sense of ownership and active participation in their care. Patients can track their progress, understand their health patterns, and make informed decisions about their treatment, ultimately leading to improved adherence to prescribed regimens.
This engagement is crucial, as adherence to treatment plans is often a significant factor in successful health outcomes. Clear, accessible data can motivate patients to actively manage their conditions, reducing the need for repeated hospitalizations and improving their overall well-being. The ability to visualize their own data can make a significant difference in patient motivation.
Real-Time Monitoring and Remote Patient Management
The real-time monitoring capabilities of IoMT devices are revolutionizing remote patient management. Healthcare providers can remotely track patients' conditions, monitor their responses to treatment, and intervene promptly if necessary, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits. This is particularly beneficial for patients in remote areas or those with chronic conditions that require ongoing monitoring.
This remote monitoring also allows for more efficient use of healthcare resources. Instead of relying solely on scheduled appointments, healthcare professionals can address potential issues proactively, reducing unnecessary hospitalizations and improving the overall efficiency of the healthcare system. The ability to respond quickly to emerging issues is a significant benefit for both patients and healthcare providers.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy in IoMT Systems
While the benefits of data-driven insights for personalized care through IoMT are substantial, it's crucial to address the critical issue of data security and privacy. The increasing volume of sensitive patient data necessitates robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and breaches. Data encryption, secure transmission protocols, and strict access controls are essential to ensure patient confidentiality and comply with relevant regulations.
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is paramount to building trust and maintaining the integrity of the data collected and transmitted. Transparency regarding data handling practices and obtaining explicit informed consent from patients are critical components of ethical IoMT implementation. This ensures that patients are aware of how their data is being used and feel confident in the security of their personal health information.
Improving Remote Monitoring and Telehealth Capabilities

Remote Monitoring System Architecture
A robust remote monitoring system relies on a well-defined architecture. This architecture needs to consider various factors, including data acquisition methods, communication protocols, and data storage solutions. A critical element is the selection of appropriate hardware and software components for optimal performance and scalability. This ensures the system can handle increasing data volumes and user demands as the monitored environment evolves.
The architecture should be designed with security in mind. Robust authentication and authorization mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Implementing encryption protocols for data transmission is also crucial. Furthermore, the system needs to be designed for fault tolerance, ensuring that if one component fails, the system can continue operating without disruption.
Data Acquisition and Transmission
Effective data acquisition is paramount for remote monitoring. This involves selecting appropriate sensors and devices that can accurately capture the necessary data points. Careful consideration of the data format and transmission protocols is also essential for efficient communication between the monitoring system and the devices being monitored. This process should also include a system for verifying the quality and integrity of data to ensure accurate analysis and reporting.
Real-time Data Processing
Real-time data processing is essential for immediate responses to anomalies or critical events. This allows for quick identification and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime and potential losses. The processing must be efficient and reliable to ensure that alerts are generated promptly and accurately.
Implementing a robust data pipeline is crucial to handle high volumes of incoming data in a timely manner. This pipeline should be capable of filtering, transforming, and storing the data for further analysis and reporting. Efficient data processing significantly enhances the effectiveness of remote monitoring.
Alerting and Notifications
A well-designed alerting system is critical for effective remote monitoring. The system should be configurable to trigger alerts based on predefined thresholds or specific events. This allows for proactive responses to potential problems, enabling timely intervention and preventing significant issues.
Security and Access Control
Robust security measures are crucial for remote monitoring systems to protect sensitive data and maintain system integrity. Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to control user access and prevent unauthorized access or modification. Data encryption during transmission and storage is vital for protecting confidentiality and preventing breaches. This will ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system and its data.
Scalability and Maintainability
A scalable remote monitoring system can adapt to growing needs and increasing data volumes. The system must be designed with scalability in mind to accommodate future expansion. A modular design allows for easier upgrades and maintenance. Clear documentation and well-defined procedures are essential for easy maintenance and troubleshooting. This will streamline the ongoing management and evolution of the system.
Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics are vital for understanding the performance of the monitored systems and identifying trends. Generating detailed reports on key performance indicators (KPIs) and system metrics provides valuable insights. This data can be used to optimize processes, identify potential issues, and improve overall efficiency. Analysis of these reports can lead to proactive improvements in the monitored systems.