AI-Facilitated Active Learning Strategies
Personalized Learning Paths
Modern educational systems leverage artificial intelligence to evaluate student performance data as it happens, pinpointing unique learning requirements and aptitudes. This enables the development of customized learning trajectories, adjusting both content and speed to maximize comprehension. By responding to each learner's individual advancement, technology helps prevent disengagement or frustration with material that's either too easy or too challenging. This responsive method of delivering lessons also makes better use of classroom hours, as educators can concentrate on addressing particular struggles rather than covering concepts most students already understand.
Moreover, feedback mechanisms grow increasingly refined. Intelligent systems can deliver precise practice materials and learning tools, guaranteeing students remain appropriately stimulated and aided in their developmental areas. This tailored educational method promotes more thorough subject mastery and cultivates greater interest in the material, resulting in enhanced memory retention and academic achievement.
Adaptive Assessment Strategies
Educational technology dramatically improves evaluation methods by automating the generation of dynamic quizzes and examinations. These tests modify their complexity according to student answers, offering a more precise and complete measure of understanding. This guarantees learners face suitable challenges, avoiding discouragement from excessively hard questions or disinterest from overly simple ones. Automated evaluations also provide instantaneous responses, helping students recognize their strong points and areas needing improvement so they can modify their study approaches.
Additionally, intelligent analysis can detect patterns in student performance data, yielding valuable information for teachers. This evidence-based method can guide pedagogical choices, enabling educators to enhance their instructional techniques and adjust their lesson plans to better serve their classes. By revealing detailed information about individual learning preferences and knowledge deficiencies, technology-enhanced assessments enable teachers to offer more targeted assistance and direction.
Real-Time Feedback and Support
Digital learning tools can offer immediate responses to students during virtual lessons, aiding their comprehension of concepts. This instantaneous exchange increases student involvement and permits prompt resolution of any confusion or misunderstandings. Educators can also use this live data to assess overall class understanding and modify their teaching approaches accordingly. By providing on-the-spot assistance, technology effectively tackles widespread misconceptions and learning obstacles, creating a more efficient and cooperative educational atmosphere.
Dynamic Content Generation and Curation
Intelligent systems can actively produce and organize educational materials customized for specific learning goals and student requirements. This enables a more varied and stimulating learning journey, exposing students to broader resources and viewpoints. The technology also assists instructors in finding and incorporating pertinent external materials, bringing practical applications and examples into lessons. This flexible approach to curriculum design ensures learning resources remain applicable, up-to-date, and interesting, maintaining student enthusiasm and curiosity about the subject.
Interactive and Engaging Learning Activities
Educational technology enables the creation of dynamic learning exercises and simulations, making education more captivating and immersive. These activities can be personalized to accommodate different learning preferences, ensuring diverse students find the experience both enjoyable and beneficial. By encouraging active involvement, technology-powered exercises can boost student motivation and information retention. Furthermore, the systems can modify activity difficulty in real-time, making certain students face continuous appropriate challenges while receiving necessary support throughout their educational progression.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Digital tools improve cooperation and interaction within virtual classrooms. These systems can support discussion boards by offering immediate translations and summaries of student contributions, facilitating participation from learners of varied backgrounds in substantive dialogues. The tools also help teachers track student involvement and spot areas needing additional explanation or help. This improved accessibility and engagement fosters a more welcoming and cooperative learning environment, enabling students to connect more meaningfully with peers and instructors.
Enhancing Accessibility and Inclusivity
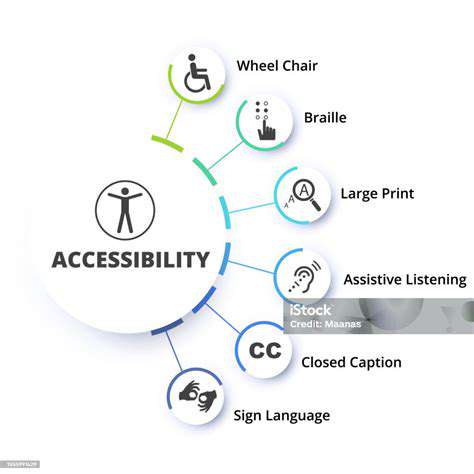
Improving Website Navigation
A vital component of increasing accessibility involves creating straightforward and intuitive website navigation. Simple, descriptive labels and meaningful links prove indispensable for users with disabilities who depend on assistive technologies. This includes establishing logical sitemap hierarchies and menus, helping users quickly grasp the structure and locate needed information. Employing explanatory text for interactive elements remains equally critical, avoiding technical terms or vague phrasing. Proper implementation of ARIA attributes can additionally enhance the accessibility of navigation components.
Optimizing Content for Screen Readers
Information must be organized for effortless interpretation by assistive technologies. Utilizing semantic HTML elements like
, , and proves essential, allowing screen readers to comprehend information hierarchy and context. Including descriptive alt text for visual media remains imperative, offering textual alternatives for graphical content. These descriptions improve the experience for visually impaired users while simultaneously helping search engines understand page content, boosting discoverability.Providing written transcripts for audio and video materials enhances accessibility for hearing-impaired users or those preferring text-based consumption, while simultaneously benefiting search engine optimization efforts.
Designing for Diverse User Needs
Creating inclusive digital experiences extends beyond screen reader compatibility. It involves supplying multiple content formats, such as downloadable documents or video transcripts, allowing users to access information according to their preferences. Accounting for varying technical skills and technology familiarity remains crucial for delivering satisfactory user experiences.
Implementing Color Contrast Guidelines
Maintaining adequate color differentiation between text and backgrounds proves essential for users with visual impairments. Following WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards for color contrast ratios remains fundamental for developing accessible web content. This practice enhances readability for all visitors and prevents situations where text becomes indistinguishable from its background. This consideration significantly improves overall usability and accessibility.
Providing Clear Instructions and Feedback
Straightforward guidance and effective response systems remain vital for helping users navigate websites. Using plain language and unambiguous directions makes sites easier to use. Offering prompt, informative responses to user actions—whether confirming success or explaining errors—enhances the experience by helping visitors understand system responses. This ensures users feel confident and in command of their interactions.
Providing written transcripts for audio and video materials enhances accessibility for hearing-impaired users or those preferring text-based consumption, while simultaneously benefiting search engine optimization efforts.
Designing for Diverse User Needs
Creating inclusive digital experiences extends beyond screen reader compatibility. It involves supplying multiple content formats, such as downloadable documents or video transcripts, allowing users to access information according to their preferences. Accounting for varying technical skills and technology familiarity remains crucial for delivering satisfactory user experiences.
Implementing Color Contrast Guidelines
Maintaining adequate color differentiation between text and backgrounds proves essential for users with visual impairments. Following WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards for color contrast ratios remains fundamental for developing accessible web content. This practice enhances readability for all visitors and prevents situations where text becomes indistinguishable from its background. This consideration significantly improves overall usability and accessibility.
Providing Clear Instructions and Feedback
Straightforward guidance and effective response systems remain vital for helping users navigate websites. Using plain language and unambiguous directions makes sites easier to use. Offering prompt, informative responses to user actions—whether confirming success or explaining errors—enhances the experience by helping visitors understand system responses. This ensures users feel confident and in command of their interactions.