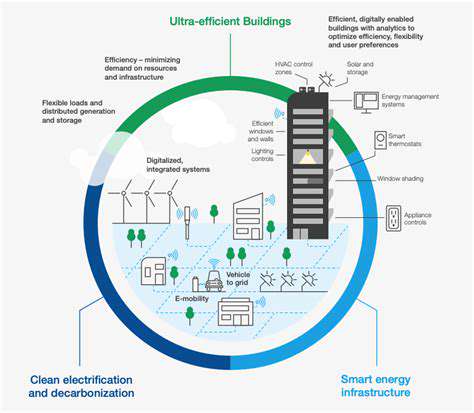
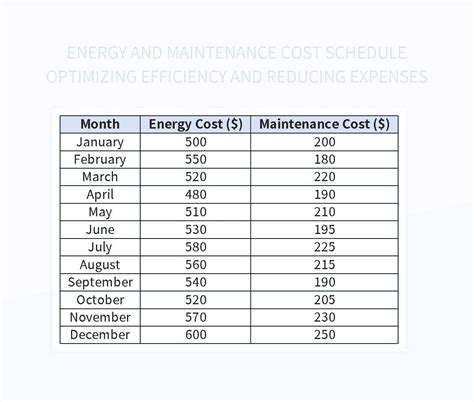
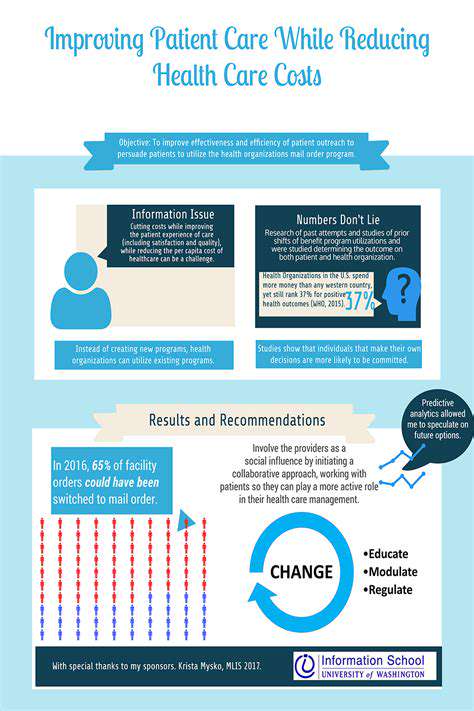
Decentralized Processing for Enhanced Speed and Efficiency

Decentralized Processing Architecture
Decentralized processing, a departure from traditional centralized models, distributes computing tasks and data across multiple nodes or entities. This approach offers significant advantages in terms of resilience, scalability, and security. By distributing the workload, a decentralized system can better withstand failures in individual nodes, as the overall system continues to operate. This inherent redundancy is a key differentiator in the face of potential outages or attacks.
This distributed nature fundamentally alters the way data is managed and processed. Each node possesses a portion of the complete data set and processing capability, leading to a more resilient and scalable system overall.
Data Security and Privacy Enhancements
Decentralized processing can significantly enhance data security and privacy by minimizing the reliance on a single, potentially vulnerable point of control. Data is often encrypted and distributed across multiple nodes, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized access or manipulation. Data ownership remains with the individual or entity that contributes the data, enabling greater control and transparency.
This inherent fragmentation of data reduces the risk of a single security breach impacting the entire system, leading to a more robust and secure environment.
Improved Scalability and Performance
The distributed nature of decentralized processing facilitates scalability. As the demand for processing power increases, new nodes can be added to the network without significantly impacting existing operations. This scalability is crucial for handling large datasets and high transaction volumes, accommodating the evolving needs of modern applications.
Enhanced Transparency and Accountability
Decentralized systems often employ transparent mechanisms for recording and validating transactions. This transparent recording of data allows for greater accountability and reduces the potential for manipulation or fraud. The shared, immutable record of transactions provides a strong foundation for trust and verification within the system.
Increased Resilience to Attacks and Failures
The distributed nature of decentralized processing inherently enhances its resilience to attacks and failures. Should one node be compromised or experience an outage, the system as a whole can continue operating. This fault tolerance is a critical advantage in environments where continuous operation is paramount.
Reduced Dependency on Central Authorities
Decentralized processing reduces reliance on central authorities or intermediaries. This minimizes single points of failure and enables greater autonomy and control for participants. This lack of reliance on a central authority also fosters trust and reduces the potential for bias or manipulation.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
Despite the many benefits, decentralized processing does present some challenges. Implementing and maintaining such systems can be complex and require specialized expertise. Interoperability between different nodes and the security of data exchange are crucial concerns that must be addressed during development. Furthermore, ensuring data consistency and integrity across the distributed network requires careful design and implementation.
Enhanced Security and Data Privacy through Edge Computing
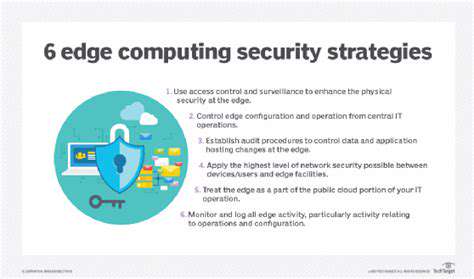
Robust Encryption Protocols
Implementing robust encryption protocols is paramount for safeguarding sensitive data. These protocols, like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), ensure that data transmitted and stored is effectively scrambled, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to decipher its contents. This layered approach to encryption, encompassing both data at rest and in transit, significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. By encrypting all sensitive information, organizations create a formidable barrier against cybercriminals. Protecting user data is a critical aspect of maintaining trust and upholding ethical business practices.
Furthermore, regular audits and security assessments of the encryption protocols are crucial to maintaining their effectiveness. This proactive approach helps identify potential vulnerabilities and ensures that the chosen methods remain up to date with the latest security threats. This continuous monitoring is essential to maintaining a strong security posture. Modern encryption solutions should also be adaptable to evolving threats, ensuring ongoing protection.
Data Minimization and Access Control
Employing data minimization principles is essential to ensure that only the necessary data is collected and stored. This proactive approach helps reduce the attack surface and limits the potential damage in the event of a data breach. This principle is particularly important for sensitive personal information, and should be carefully considered in the design of all data collection procedures. By collecting only the data required to fulfill a specific purpose, organizations demonstrate a commitment to data privacy. A comprehensive data governance framework should be established to outline the rules and guidelines for data collection, storage, and access.
Implementing strict access control measures is another critical aspect of data privacy. By carefully defining who has access to specific data and what level of access they have, organizations can significantly limit the potential for unauthorized data breaches. This granular approach to access control, combined with strong authentication mechanisms, helps to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse. Restricting access based on the need to know principle is a cornerstone of a robust data security strategy.
Privacy-Preserving Technologies
Exploring and implementing privacy-preserving technologies is vital for maintaining data security in an increasingly interconnected world. These technologies can effectively protect sensitive information without compromising the functionality of applications or services. For example, differential privacy techniques can mask individual data points while still allowing for meaningful analysis of aggregated data. This approach is crucial for protecting user privacy while still enabling valuable insights and research.
Another crucial aspect of privacy-preserving technologies is the use of federated learning. This approach allows multiple organizations to collaboratively train machine learning models without sharing their individual datasets. This approach protects sensitive data while enabling the development of more powerful and insightful models.
Beyond these examples, ongoing research and development in privacy-preserving technologies are essential. This constant innovation is vital for addressing the ever-evolving landscape of data security threats. Staying ahead of the curve with the latest advancements in this field is essential for maintaining a strong security posture. By embracing these technologies, organizations can demonstrate a commitment to data privacy and build trust with their users.